Angular Momentum in Case of Rotation about a Fixed Axis
Angular Momentum in Case of Rotation about a Fixed Axis: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Angular Momentum of a Rigid Body in Pure Rotation, Angular Momentum and Angular Velocity, and Conservation of Angular Momentum in Pure Rotation.
Important Questions on Angular Momentum in Case of Rotation about a Fixed Axis
When a body is spinning on its axis in absence of any external torque, then choose the wrong statement
Angular momentum of a system of particles changes when
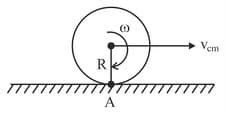
A ring of mass and radius is rolling without slipping, the velocity of point as shown in the figure
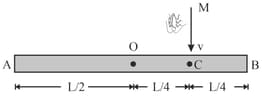
A homogeneous rod AB of length and mass is pivoted at the center O in such a way that it can rotate freely in the vertical plane. The rod is initially in the horizontal position. An insect S of the same mass falls vertically with speed on the point C mid-way between O and B. Determine the initial angular velocity in terms of and .
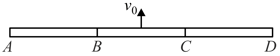
Three uniform rods and each of mass m and length are moving together with velocity on a smooth horizontal surface (direction of is perpendicular to length ) The roads and are hinged at and respectively so that they can rotate freely about and . At an instant during the motion, the middle road is suddenly fixed on the horizontal surface. Find the time taken for the ends and to meet.
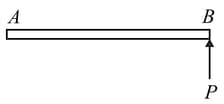
A uniform rod of mass and length / is at rest on smooth horizontal surface. An impulse is applied to end as shown in the figure. The point about which the rod can be assumed to be rotating just after the impulse applied is
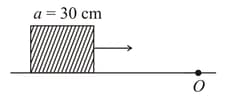
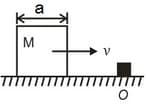
A cubical block of side is moving with velocity on a smooth horizontal surface. The surface has a bump at a point as shown in the figure. The angular velocity (in ) of the block immediately after it hits the bump, is:
An object of mass is projected from ground, with initial velocity , making angle with the horizontal. Find its angular momentum about the point of projection when the object is at its maximum height. (Take )
A thin circular ring of mass and radius is rotating about its axis with a constant angular velocity Two objects each of mass are attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The ring now rotates with an angular velocity
An object of mass is projected from ground, with initial velocity , making angle with the horizontal. Find its angular momentum about the point of projection when the object is at its maximum height. (Take )
A uniform circular disc of moment of inertia about its axis is rotating with angular speed . Another uniform circular disc of moment of inertia about its axis is rotating with angular speed in same sense. They are gently brought into contact face to face, coinciding the axis of rotation. The loss of kinetic energy till they attain the common angular velocity, is
A thin circular ring of mass and radius is rotating in a horizontal plane about an axis vertical to its plane and passes through center with a constant angular velocity If two objects each of mass be attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring, the ring will then rotate with an angular velocity :-
If the earth were to suddenly contract to of its present radius without any change in its mass, then the duration of the new day will be nearly
A solid sphere of mass and radius is rotating about its diameter. A solid cylinder of the same mass and same radius is also rotating about its geometrical axis. However it has an angular speed twice that of the sphere. What is the ratio of their kinetic energies of rotation ?
The angular momentum of a particle moving on a circular path with a constant angular velocity is . If the radius of the path is halved while the angular velocity unchanged, The new angular momentum of the particle is
A uniform rod of length and mass is hanged at point , such that it can rotate in vertical plane, in a car. The car is moving upward with velocity on an inclined plane as shown. If the car comes to halt at once then calculate angular speed with which the rod starts rotating.
A circular platform is free to rotate in a horizontal plane about a vertical axis passing through its centre. A tortoise is sitting at the edge of the platform. Now the platform is given an angular velocity . When the tortoise moves along a chord of the platform with a constant velocity (w.r.t. the platform), Which of the following graphs shows properly the variation of angular velocity of the platform with the time is-
There is a cubical block with length of its side being . It is moving with a velocity on a horizontal smooth plane as shown. It hits a ridge at point O. The angular speed of the block after it hits O is
A rotating body has angular momentum . If its frequency of rotation is halved and rotational kinetic energy is doubled, its angular momentum becomes
A man stand on a rotating platform with his arms stretched is holding a weight in each hand. The angular speed of the platform is . The moment of inertia of the man together with the platform may be taken to be constant and equal to . If the man brings his arms close to his chest with the distance of each weight from the axis changing from to , the new angular speed of the platform is
